Demystifying the Stock Market : A Beginner’s Guide

The stock market is often perceived as a complex and daunting financial landscape. However, with the right knowledge and understanding, it can be navigated successfully, much like exploring a bustling street market filled with opportunities and risks. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fundamentals of the stock market, draw parallels with everyday concepts, such as option chain premiums in an insurance company, and explore the myriad factors influencing stock prices.
Understanding the Stock Market
What is the Stock Market?
Imagine the stock market as a vast marketplace where companies list their shares for sale to the public. These shares represent ownership in the company, and when you buy shares, you become a shareholder, entitled to a portion of the company’s earnings and assets.
Key Participants in the Stock Market:
- Investors: Individuals or institutions buying and selling stocks.
- Companies: Issuers of stocks seeking capital from investors.
- Stock Exchanges: Platforms where stocks are traded, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or NASDAQ.
Functions of the Stock Market
- Capital Formation: Companies raise funds for expansion and operations by selling shares.
- Facilitating Investments: Investors can buy and sell shares to build wealth and achieve financial goals.
- Price Discovery: Stock prices reflect market sentiment and expectations about a company’s future performance.
Comparing the Stock Market to a Street Market
Similarities with a Street Market
In a street market, prices fluctuate based on supply, demand, and perceived value. Similarly, stock prices fluctuate based on investor perceptions, economic conditions, and company performance. Just as savvy shoppers hunt for bargains, investors seek undervalued stocks poised for growth. For example, Price Dynamics, When a particular fruit is in high demand at a street market, its price rises. Likewise, positive news or strong financial results can drive up a company’s stock price as demand increases.

Option Chain Premiums Vs Insurance Premium
Similarities with a Street Market
Option chain premiums in the stock market resemble insurance premiums in the insurance industry. Options give investors the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell a stock at a predetermined price (strike price) within a specified period (expiration date).
Components of Option Premiums:
Intrinsic Value: The difference between the stock’s current price and the option’s strike price (if applicable). Time Value: Reflects the potential for the option to gain value before expiration. Volatility: Higher volatility increases option premiums due to increased risk.
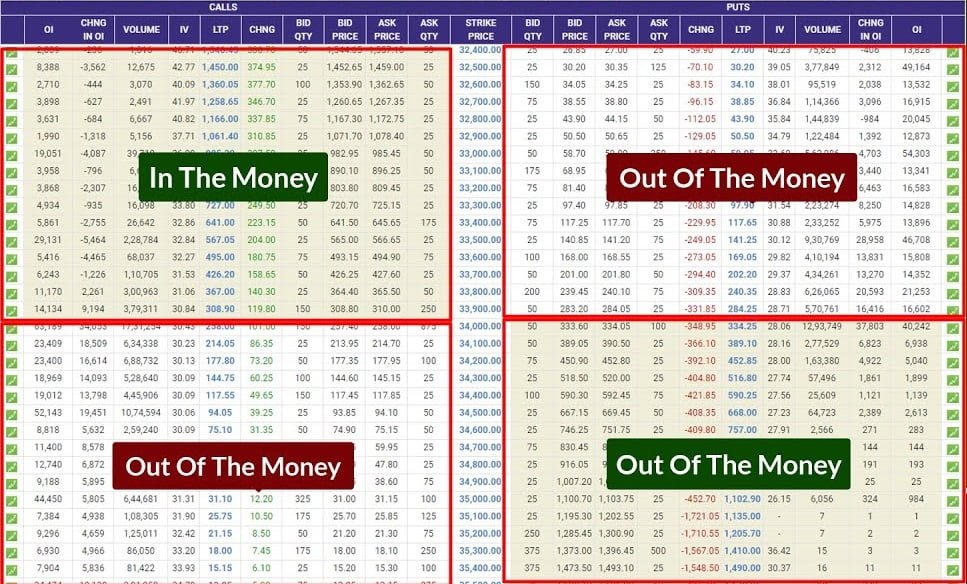

Comparison with Insurance Premiums
Factors Influencing Stock Prices
- Company Performance: Strong earnings, innovative products, and effective management can boost investor confidence and drive stock prices higher.
- Market Sentiment: Investor perceptions and emotions influence buying and selling decisions. Positive news about a company or sector can lead to increased buying activity, pushing prices up.
- Economic Indicators: Factors such as interest rates, inflation rates, and GDP growth impact stock prices. Lower interest rates, for example, can stimulate economic activity and potentially increase corporate earnings, positively affecting stock prices.
- Industry Trends: Developments within specific industries or sectors can impact stock prices. Technological advancements, regulatory changes, and consumer preferences all play significant roles.
- Global Events: Geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and global economic trends can create volatility in the stock market. Uncertainty often leads to fluctuations in stock prices as investors react to unfolding events.
Strategies for Successful Investing

Tips for Beginners
- Educate Yourself: Understanding how the stock market works and the basics of investing is crucial. Take advantage of resources such as books, online courses, and financial news to enhance your knowledge.
- Define Your Goals: Determine your financial objectives, risk tolerance, and investment timeline. This will guide your investment decisions and strategy.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread your investments across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate) and industries to reduce risk.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with market trends, economic news, and company developments that may impact your investments.
- Long-Term Perspective: Investing in the stock market is generally a long-term endeavor. Avoid making hasty decisions based on short-term market fluctuations.
Conclusion
Navigating the stock market can seem daunting at first, but with a solid understanding of its fundamentals and key principles, beginners can build confidence and make informed investment decisions. By drawing parallels with everyday concepts like street markets and insurance premiums, we demystify complex financial concepts and empower individuals to embark on their investment journey with clarity and purpose.
Remember, successful investing requires patience, discipline, and continuous learning. With diligence and a long-term perspective, you can harness the potential of the stock market to achieve your financial goals.


Pingback: How to Identify Support and Resistance - Trading Capsules